dataproductpoc-docs
Authentication & Authorisation
Apart from public data, most organisation’s data needs to be secured.
In terms of a data product, security will need to cover authentication and authorisation of a user.
This particular topic is one of the hardest parts of implementing a data product as each organisation has their own established ways of authenticating and authorising users/systems which in my experience can take weeks to establish.
Authentication
Authentication means ensuring that a user is who they say they are. There are many methods of authenticating a user. These include:-
Basic Authentication
This is a simple username and password which are typically combined, base-64 encrypted and passed to a data product in the header of a http request. This type of authentication is the easiest to implement but also the least secure, due to base64 being relatively easy to hack.
Multi-factor authentication
Takes authentication to the next level by requiring a user/system to authenticate by more than 1 method e.g.
- the user is asked to type their username and password in a web browser
- The user is also required to confirm their identity typically by:-
- Sending a text or email which the user either has to click a link or copy a one-time password in to the web page
- Using an identity provider app to confirm their identity. When done, they are returned to the original website
- Being redirected to an identity provider website to confirm their identity. When done, they are returned to the original website Common examples of trusted identity providers include:-
- PingID
- Microsoft
- Linkein
Token based authentication
Token based authentication can involve:-
- A developer registering their application with another application that they wish to communicate with. During registration, a SHA256 (or similar) encrypted token can be generated and together with an API key or Client ID and Client secret ensures that only registered applications can gain access.
More complex flows e.g. OAUTH2, ensure that the registered application is who they say they are and not another application imitating it by going through a more complex authentication flow which involves swapping the registered token with an access token by sending the response back to the registered application’s callback url :-
- the server application providing information that was previously registered with the authentication system
- the authentication system responding to a server application url which was previously registered.
- the server application redirecting the user to the authentication system to securely authenticate
- the authentication system responding with an access token to a callback url on the server application
- the server application can subsequently use the access token (which periodically typically needs to be refreshed) to authenticate as the user
Implementing Authentication within an Organisation
For the PoC we have chosen to use basic authentication for demo purposes.
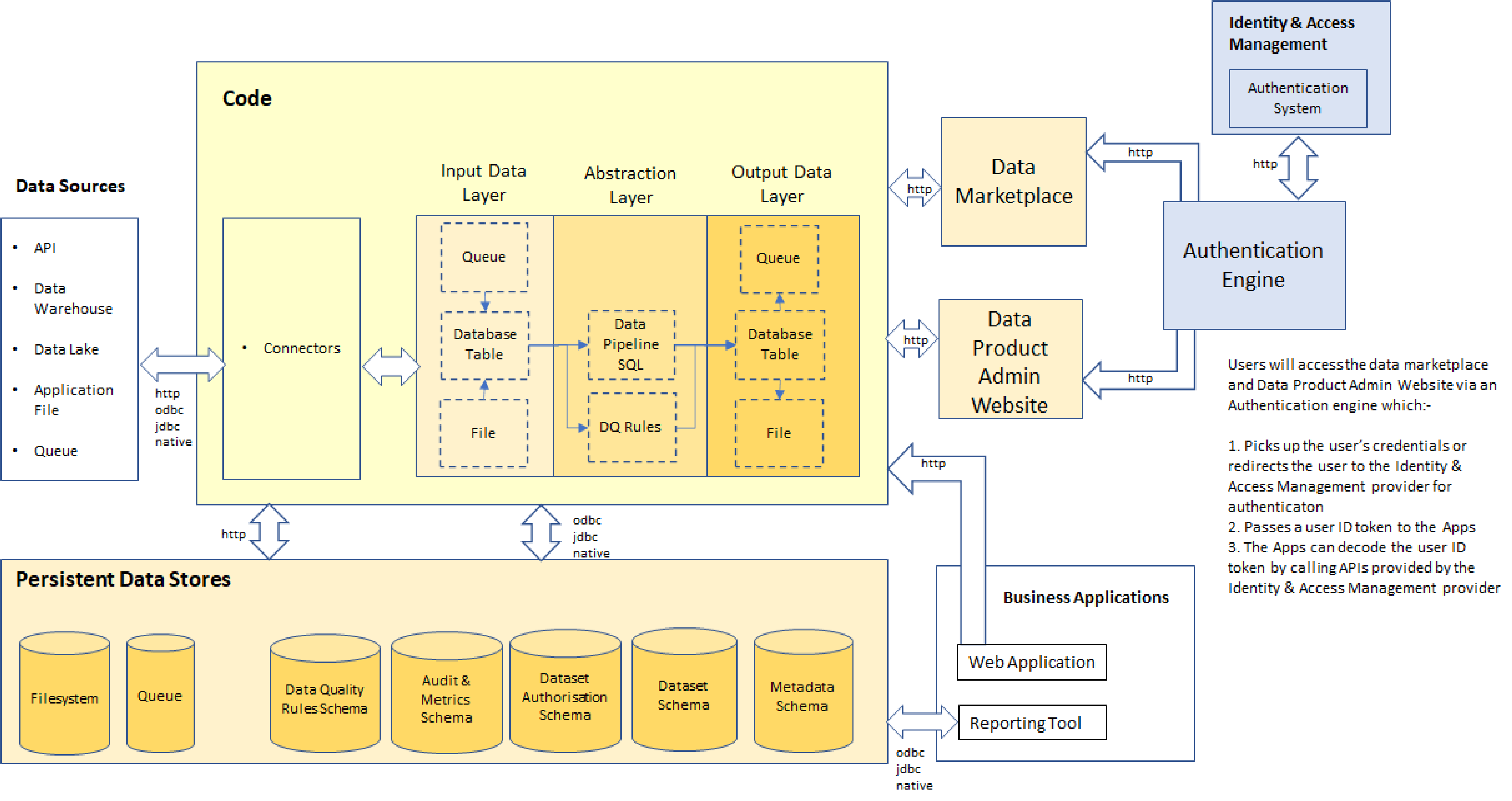
Within an organisation, we typically use Token based authentication. This will involve:-
- Registering the Data Marketplace and Data Product Admin Website with the Authentication engine that you use. Note: The Authentication engine should sit in front of these Apps and be able to pass a user ID token in the http header
- Adding code to our Apps to decode the provided user ID token using your Identity Provider
The diagram shows how this set up works in practice:-
Authorisation
Authorisation means ensuring that an authenticated user is permitted to access the requested data. Authorisation is a loaded term. So needs to be split down further for clarity.
Data Product Authorisation
This type of authorisation just ensures that a particular user/role is permitted to access a particular data product. Dependent on the authorisation system used it may be able to authorise the data product in it’s entirety or specific endpoints. So, for example, it may be desirable to allow free access to the Discovery port/endpoint so that anybody can view the data product documentation, but restrict access to the output data ports to a particular set of users, and restrict access to the input data port and control data port to specific roles.
Dataset authorisation
As a data product can provide more than 1 target dataset, it is also desirable to provide more fine grained access control at the dataset level.